The exact cause of hepatic carcinoma is not known but it has been seen in the cases of Alcoholic cirrhosis, Macronodular cirrhosis, Haemochromatosis, B heptatitis, C hepatitis , Alpha I antiprotease deficiency, Tyrosinaemia and Aflatoxin exposure for a long time.
Types
Benign
Adenoma, Haemangioma etc.
Malignant
Primary (Rare)
a) Carcinoma
- Hepatoma- common
- Cholangioma- rare
b)Sarcoma (rare)
Secondary (Common)
The primary sites are as below:
- Stomach
- Gall Bladder
- Colon
- Pancreas
- Adrenal
- Kidney
- Uterus
- Breast
- Prostate
- Bronchus
- Eye
- Lungs
Symptoms
- Symptoms of primary disease may or may not be present.
- Anorexia, weakness, loss of flesh are important symptoms.
- Jaundice.
- Low grade fever
- Swelling of the abdomen
- Pain in the right hypochondriac region.
Marked anorexia , cachexia, weight loss, etc. if develop suddenly in an otherwise stable cirrhosis patient this condition should be suspected. Again sudden development of ascitis (particularly bloody) in a stable patient of cirrhosis will also arouse suspicion for malignancy.
On Examination
General survey
Patient is aged Cachexia is present. Jaundice may be seen. Anaemia is moderate to marked in degree. Oedema is present. Hard and fixed lymph nodes may be palpable on the left side of the root of the neck (Virchow’s node)
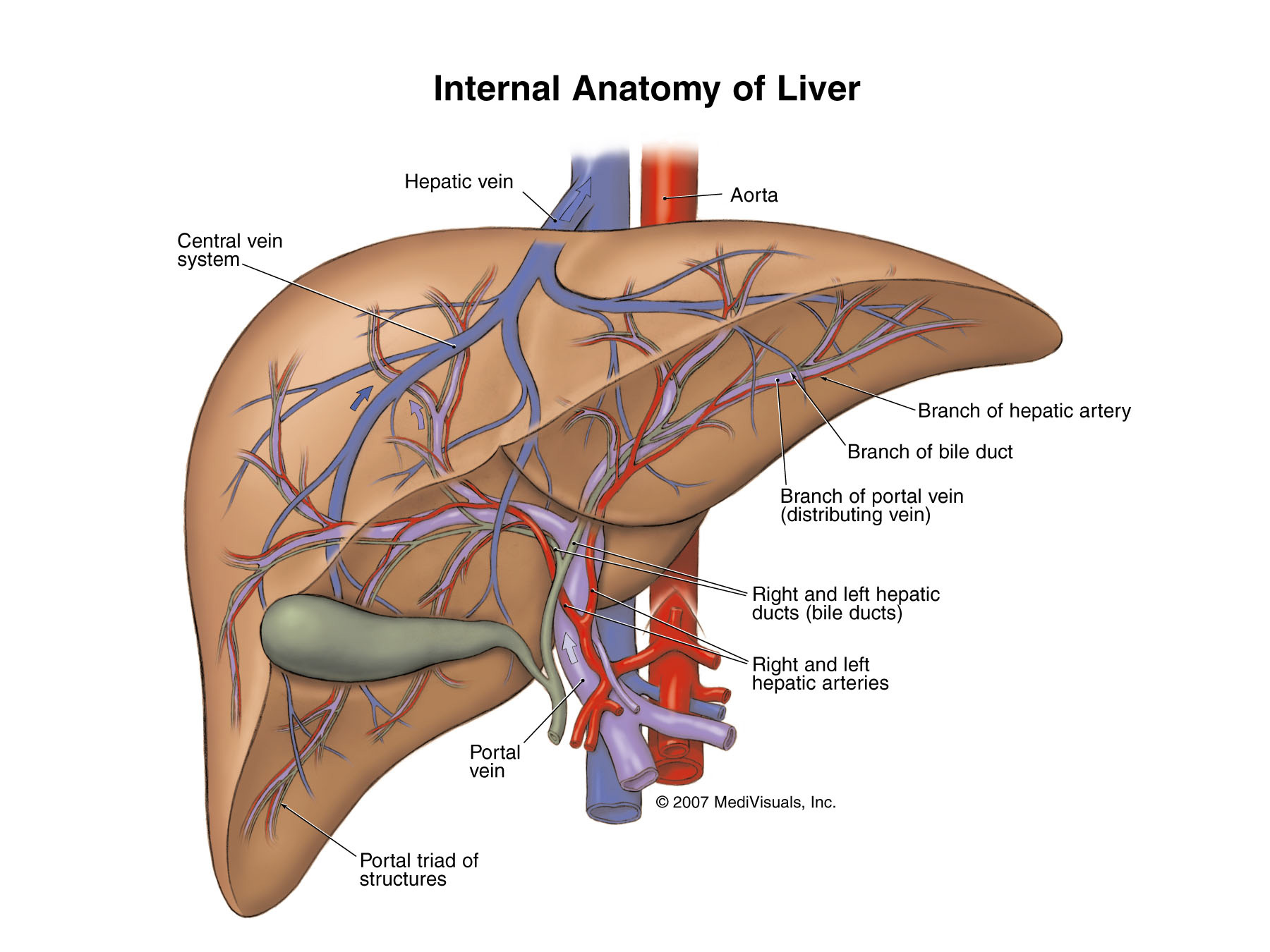
Abdomen : Liver is enlarged , hard, irregular, noudular very tender. Noudules may be umbilicated. Hapatic rub may be present. Sometimes a murmur is also heard over the liver. Both rub and murmur when simultaneously present constitute pathognomonic signs of hepatic carcinoma. Spleen is not palpable (if it was not previously palpable0
Ascites of any degree may be present. As carcinoma occurs in 20% cases of macronodular cirrhosis one should think of its presence when ascities is persistent or it increases in an otherwise stable cirrhosis patient. A hard lump may be felt in the abdomen over the stomach or gall bladder region.
Special Investigations
Examination of the peritoneal fluid may show malignant cells.
Needle biopsy of the liver may show malignant deposits. Sometimes laparoscopy or laparotomy may be required for liver biopsy.
Biopsy of enlarged lymph nodes may also show secondary deposits.
Blood examination may reveal leucocytosis and high ESR.
Serum alkaline phosphatase is raised. Alphafetoprptien is raised in 60%-80% cases of hepatoma (500 mg/cc or more (normal 1 to 10 mg/cc) but not in cholangioma.
Arteriography may reveal a tumour “blush”.
Liver scan is helpful in the diagnosis.
Don’t wait please try it
Today fill our form send with your photographs of disease by email and get your medicine at your door.
Medicines prescribed are
CALCAREA-ARSENICOSUM: I frequently find cancer of the liver yielding to Cal-ars in every way, but if there is a tendency to relapse frequently, a single dose of CADM. in high potency will render the cure permanent. (Dr.Grimmer)
CHOLESTERINUM: Burnett has cured cancer of the liver even in the last stage. (CLARKE)