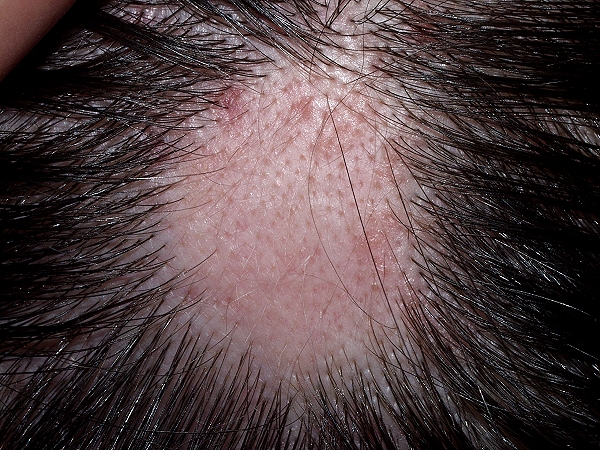
Alopecia areata is considered an autoimmune disease, in which the immune system, which is designed to protect the body from foreign invaders such as viruses and bacteria, mistakenly attacks the hair follicles, the tiny cup-shaped structures from which hairs grow. This can lead to hair loss on the scalp and elsewhere.
In most cases, hair falls out in small, round patches about the size of a quarter. In many cases, the disease does not extend beyond a few bare patches. In some people, hair loss is more extensive. Although uncommon, the disease can progress to cause total loss of hair on the head or complete loss of hair on the head, face, and body (alopecia areata universalis).
Causes
In alopecia areata, immune system cells called white blood cells attack the rapidly growing cells in the hair follicles that make the hair. The affected hair follicles become small and drastically slow down hair production. Fortunately, the stem cells that continually supply the follicle with new cells do not seem to be targeted. So the follicle always has the potential to regrow hair.
Scientists do not know exactly why the hair follicles undergo these changes, but they suspect that a combination of genes may predispose some people to the disease. In those who are genetically predisposed, some type of trigger–perhaps a virus or something in the person’s environment–brings on the attack against the hair follicles.
Alopecia areata is not a life-threatening disease. It does not cause any physical pain, and people with the condition are generally healthy otherwise. But for most people, a disease that unpredictably affects their appearance the way alopecia areata does is a serious matter.
The effects of alopecia areata are primarily socially and emotionally disturbing. In alopecia universalis, however, loss of eyelashes and eyebrows and hair in the nose and ears can make the person more vulnerable to dust, germs, and foreign particles entering the eyes, nose, and ears.
Alopecia areata often occurs in people whose family members have other autoimmune diseases, such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, pernicious anemia, or Addison’s disease. People who have alopecia areata do not usually have other autoimmune diseases, but they do have a higher occurrence of thyroid disease, atopic eczema, nasal allergies, and asthma.
There is every chance that your hair will regrow, but it may also fall out again. No one can predict when it might regrow or fall out. The course of the disease varies from person to person. Some people lose just a few patches of hair, then the hair regrows, and the condition never recurs. Other people continue to lose and regrow hair for many years. A few lose all the hair on their head; some lose all the hair on their head, face, and body. Even in those who lose all their hair, the possibility for full regrowth remains.
In some, the initial hair regrowth is white, with a gradual return of the original hair color. In most, the regrown hair is ultimately the same color and texture as the original hair.
The course of alopecia areata is highly unpredictable, and the uncertainty of what will happen next is probably the most difficult and frustrating aspect of the disease. You may continue to lose hair, or your hair loss may stop. The hair you have lost may or may not grow back, and you may or may not continue to develop new bare patches.
Treatment
RNA, Kali phos, Phosphorus. Pix liquida, Arnica, Wiesbaden, Acid Phos, Calc Phos and Ignetia etc… will be use for cure .
If you are interested for medicine then fill the send detail and send to us
#Natrum muriaticum [Nat-m]
Has the symptoms of easy falling out of the hair; it falls out when touched or combed. This is quite frequently seen in nursing home. Carbo vegetabilis has falling of hair after parturition or severe illness. Sepia has losing of hair after chronic headaches.
#Phosphorus [Phos]
Bald spots on the head, which are dry and scaly, are characteristic of Phosphorus. Dandruff, roots of hair get gray and the hair comes out in bunches. Graphites cures bald spots on the sides of the head. The head sweats easily. The most important remedy in alopecia areata.
# Phosphoric acid [Ph-ac]
Falling of hair from general debility. Fluoric acid. Falling of hair from syphilis. As near specific as is possible. Arsenicum. Bald spots near the forehead; the scalp is covered with dry scales. Vinca minor. Falling of the hair with great itching of the scalp.