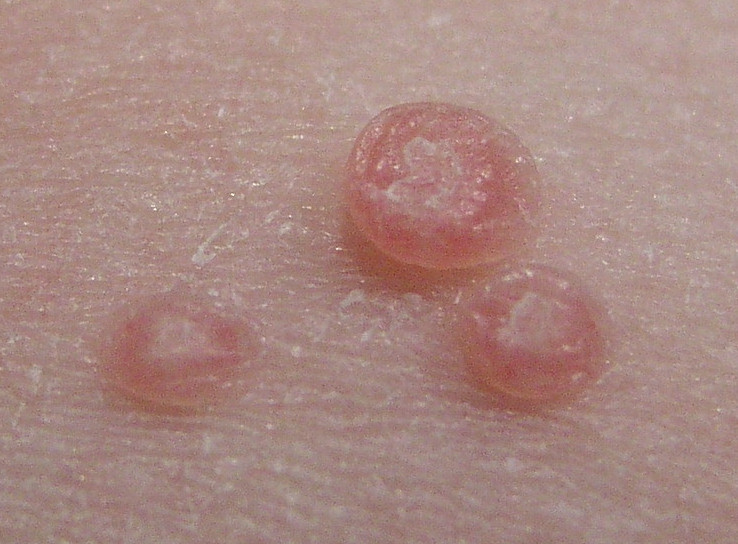
A skin disease caused by the molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) usually causing one or more small lesions/bumps. MCV is generally a benign infection and symptoms may self-resolve. MCV was once a disease primarily of children, but it has evolved to become a sexually transmitted disease in adults. It is believed to be a member of the pox virus family.
How is it transmitted?
Molluscum contagiosum may be sexually transmitted by skin-to-skin contact (does not have to be mucous membranes) and/or lesions. Transmission through sexual contact is the most common form of transmission for adults.
MCV may be transmitted from inanimate objects such as towels and clothing that come in contact with the lesions. MCV transmission has been associated with swimming pools and sharing baths with an infected person.
MCV also may be transmitted by autoinoculation, such as touching a lesion and touching another part of the body.
Symptoms
Lesions are usually present on the thighs, buttocks, groin and lower abdomen of adults, and may occasionally appear on the external genital and anal region.
Children typically develop lesions on the face, trunk, legs and arms.
The lesions may begin as small bumps which can develop over a period of several weeks into larger sores/bumps. The lesions can be flesh colored, gray-white, yellow or pink. They can cause itching or tenderness in the area, but in most cases the lesions cause few problems. Lesions can last from 2 weeks to 4 years — the average is 2 years.
People with AIDS or others with compromised immune systems may develop extensive outbreaks
Reduce your risk
Because transmission through sexual contact is the most common form of transmission for adults, preventing skin-to-skin contact with an infected partner will be most effective in preventing MCV.
Latex condoms or other moisture barriers for vaginal, oral, and anal sex may help to prevent such contact. Limitations of such barriers must be recognized as MCV does not require mucous membrane contact to be passed.
Using water-based spermicide for vaginal intercourse. Spermicide is not recommended for oral sex, and has not been found safe or effective for anal intercourse.
Using condoms may protect the penis or vagina from infection, but do not protect from contact with other areas such as the scrotum or anal area.
Mutual monogamy (sex with only one uninfected partner)
If you do get molluscum contagiosum, avoid touching the lesion and then touching another part of the body without washing your hands to prevent chance of autoinoculation.