These are primary affections of muscles in the form of pathological , biochemical or electrical changes characterised by involvement of proximal muscle group, ultimate wasting , absence of fibrillation, bilateral involvement , absence of involvement of central or peripheral nervous system, downhill course and absence of remission. Some of these are genetically determined and may have hereditary transmission. No definite cause is known.
PSEUDOHYPERTROPHIC TYPE
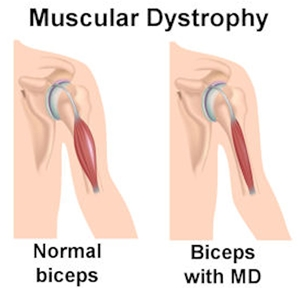
This occurs only in males. It is transmitted by a sex-linked recessive gene. Females carry the disease through gene but males are the victims of it. One third of the cases, however, develop by spontaneous mutation. Recently a locus has been found in Xp 21 region of X chromosome. The disease may start in foetal life but in about 50% of cases it is manifested in second or third year of life, at times it may start later between 4-7 years. First of all the pelvic girdle muscles are affected and ultimately there is involvement of shoulder girdle muscles. In a considerable number of cases to start with pseudo hypertrophy is seen. This is seen in glutei, calf muscles, quadriceps, deltoids and infraspinati. These muscles look bulkier from outside but motor power and tone are less, jerks are dull. On voluntary contraction the affected fleshy feel is lost. Concomitant to this pseudo hypertrophy, some muscles also show atrophy. Pectoralis major is one such muscles which becomes so thin that it may be aptly compared to a parchment paper. In course of time all muscles showing pseudo hypertrophy will have this fate and they all will be atrophic. Gradually contracture develops.
As a result of weakness of the affected muscle groups, Patient cannot walk in a normal manner. There is frequent fall during walk. Climbing up or rising up from the floor becomes difficult. Gait is peculiar. Patient stands on a board base with a lordosis of the lumber spine, the whole chest is thrown in a forward plane and during stepping the patient swings this way and that , like that of a duck. This type of gait is called waddling or duck gait. In the early stages instead of this gait patient may show just a limping gait and in the terminal stages when all muscles are wasted patient cannot stand erect and in an attempt to do so the patient crawls on the ground. This called frog-like gait.
From lying down position when the patient tries to get up he rolls over his body to one side, then supports on the ground , then on his feet, knees and waist and then stands up as if he is climbing up his own body. This is called rising Test or Gower’s sign and is very characteristic.
Due to weakness of the shoulder girdle muscles hanging by the support of the axillae becomes difficult and the patient falls down. Death occurs usually in the second decade from inanition or respiratory infection. Heart is sometimes affected.
Investigations :
1. Muscle biopsy shows islands of necrosed myofibrils in a vast ocean of fibrofatty tissue.
2. EMG shows a myopathic pattern.
3. Enzyme study : Serum Aldolase is raised. CPK is elevated (100 to 200 times the normal level)
Carrier detection : In carrier females 70% will have raised CPK. The remaining 30% will have abnormality of EMG or muscle biopsy.
4. Dystrophin level is very much reduced or absent in the muscles. By genetic studies the disease can be recognised in early pregrency in about 95% of cases, and in late pregrency by DNA probe from foetal tissue obtained by amniocentesis.
FOLLOWING HOMOEOPATHIC MEDICINES ARE USED IN TREATING IT : Plumbum Met, Gelsimium, Argent Nit, Rescue, are needed according to symptom but no satishfactory result is there some times cpk found low after using of Plumbem met.