Tinnitus, Ringing in the ears, Hissing, Roaring,Whistling, Chirping, Clicking
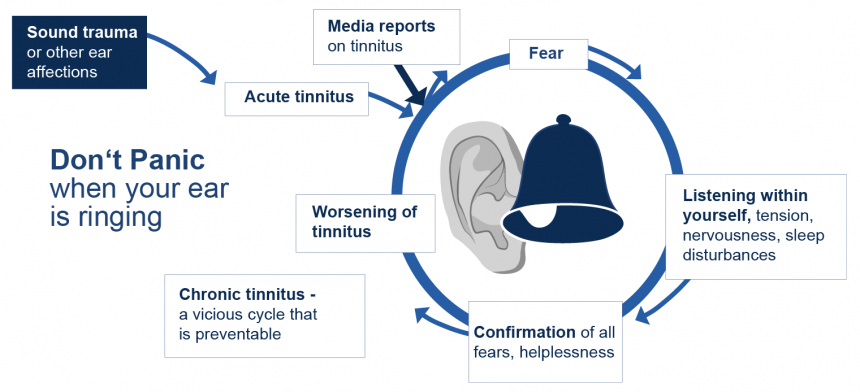
Tinnitus is the medical term for the perception of sound in one or both ears or in the head when no external sound is present. It is often referred to as “ringing in the ears,” although some people hear hissing, roaring, whistling, chirping, or clicking. Tinnitus can be intermittent or constant-with single or multiple tones-and its perceived volume can range from subtle to shattering.
The exact physiological cause or causes of tinnitus are not known. There are, however, several likely sources, all of which are known to trigger or worsen tinnitus.
Noise-induced hearing loss – Exposure to loud noises can damage and even destroy hair cells, called cilia, in the inner ear. Once damaged, these hair cells cannot be renewed or replaced. Millions of Americans have hearing loss due to noise exposure, and up to 90 percent of all tinnitus patients have some level of noise-induced hearing loss.
Wax build-up in the ear canal – The amount of wax ears produce varies by individual. Sometimes, people produce enough wax that their hearing can be compromised or their tinnitus can seem louder. If you produce a lot of earwax, speak to your physician about having excess wax removed manually-not with a cotton swab, but by an otolaryngologist (also called an ear, nose, and throat doctor).
Certain medications – Some medications are ototoxic-that is, the medications are toxic to the ear. Other medications will produce tinnitus as a side effect without damaging the inner ear. Effects, which can depend on the dosage of the medication, can be temporary or permanent. Before taking any medication, make sure that your prescribing physician is aware of your tinnitus, and discuss alternative medications that may be available.
Ear or sinus infections – Many people, including children, experience tinnitus along with an ear or sinus infection. Generally, the tinnitus will lessen and gradually go away once the infection is healed.
Jaw misalignment – Some people have misaligned jaw joints or jaw muscles, which can not only induce tinnitus, but also affect cranial muscles and nerves and shock absorbers in the jaw joint. Many dentists specialize in this temporomandibular jaw misalignment and can provide assistance with treatment.
Cardiovascular disease – Approximately 3 percent of tinnitus patients experience pulsatile tinnitus; people with pulsatile tinnitus typically hear a rhythmic pulsing, often in time with a heartbeat. Pulsatile tinnitus can indicate the presence of a vascular condition-where the blood flow through veins and arteries is compromised-like a heart murmur, hypertension, or hardening of the arteries.
Certain types of tumors – Very rarely, people have a benign and slow-growing tumor on their auditory, vestibular, or facial nerves. These tumors can cause tinnitus, deafness, facial paralysis, and loss of balance.
Head and neck trauma – Physical trauma to the head and neck can induce tinnitus. Other symptoms include headaches, vertigo, and memory loss.
Treatment: Arnica, Belladonna, Mephatis, etc… will be use for cure .If you are interested for medicine then fill the send detail and send to us